Understanding Unwanted Tattoos: An Overview
Unwanted tattoos are those that an individual no longer desires or accepts on their body. They can range from simple designs to elaborate artworks, covering small areas of the skin to large portions of the body.
The prevalence of unwanted tattoos is difficult to estimate accurately, but a 2015 study estimated that approximately 11% of Americans have at least one unwanted tattoo. This suggests that the issue of unwanted tattoos is not insignificant and affects a sizable population.
Unwanted tattoos can have a significant psychological impact on individuals, leading to feelings of embarrassment, shame, regret, and low self-esteem. Furthermore, they can hinder employment opportunities, social interactions, and participation in certain activities where visible tattoos may be frowned upon.
Identifying the Symptoms of Unwanted Tattoos
The primary symptom of an unwanted tattoo is simply the desire to remove it. This desire can arise due to various factors, including:
- Regret: Feeling remorse or disappointment over getting the tattoo.
- Changing Tastes: Evolving aesthetic preferences or a shift in personal style.
- Life Experiences: Significant life events, such as career changes, relationships, or religious beliefs, may lead to a desire for removal.
- Social Perceptions: Changing societal attitudes towards tattoos or negative reactions from others.
- Visibility: The location and size of the tattoo may make it difficult to conceal, causing discomfort or embarrassment.
Causes and Risk Factors of Unwanted Tattoos
The decision to get a tattoo is often influenced by a combination of factors, and the same is true for the desire to remove it. Some common causes and risk factors associated with unwanted tattoos include:
- Impulsivity: Getting a tattoo without careful consideration or under the influence of peer pressure or emotions.
- Lack of Information: Not fully understanding the permanence and potential consequences of getting a tattoo.
- Poor Tattoo Artist: Choosing an inexperienced or unskilled tattoo artist can result in unsatisfactory work.
- Imitation: Getting a tattoo to follow a trend or mimic someone else’s style, without personal conviction.
- Age: Younger individuals are more likely to get tattoos impulsively and may later regret their decision.
Different Types and Stages of Unwanted Tattoos
Unwanted tattoos can be broadly categorized into two main types:
- Professional Tattoos: These are tattoos that were done by a licensed tattoo artist using proper techniques and equipment.
- Amateur Tattoos: These are tattoos that were done by an inexperienced or unlicensed individual, often using makeshift tools and techniques.
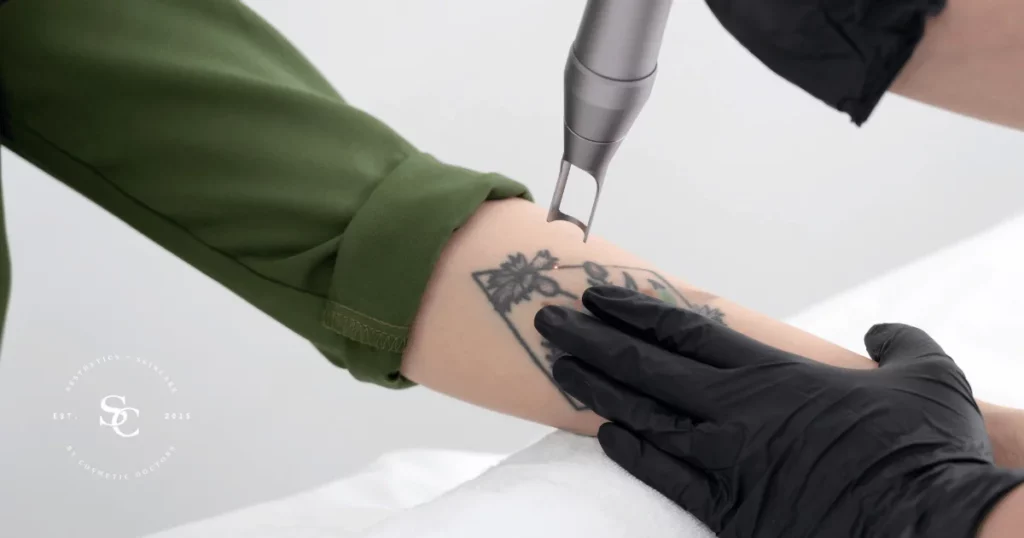
Depending on the extent of the tattoo and the desired removal method, the process can involve multiple stages or sessions. Laser removal typically requires several sessions spaced over weeks or months, while surgical removal may be completed in a single procedure.
Diagnosis: How Unwanted Tattoos are Detected
The diagnosis of an unwanted tattoo is straightforward and typically involves a visual examination by a healthcare professional. The individual’s desire to remove the tattoo and their reasons for doing so are also taken into consideration.
In some cases, additional tests may be necessary to assess the skin’s condition and determine the suitability of different removal methods. For instance, a patch test may be performed to check for skin sensitivity to laser treatments.
Treatment Options for Unwanted Tattoos
There are several methods available for removing unwanted tattoos, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The choice of treatment depends on factors such as the size, color, age, and location of the tattoo, as well as the individual’s budget and preferences.
The most common tattoo removal methods include:
- Laser Removal: This is the most widely used method and involves using high-intensity laser beams to break down the tattoo ink particles.
- Surgical Removal: This involves cutting out the tattooed skin and stitching the remaining skin together.
- Dermabrasion: This method uses a rotating abrasive tool to remove the top layer of skin, including the tattoo ink.
- Chemical Peels: This involves applying a chemical solution to the tattoo, which causes the skin to peel and the tattoo to fade.
- Cryosurgery: This method uses extreme cold to freeze and destroy the tattoo ink.
Prevention Strategies for Unwanted Tattoos
The best way to avoid unwanted tattoos is to think carefully before getting one. Some preventive measures include:
- Research Tattoo Artists: Choose an experienced and reputable tattoo artist who uses proper techniques and equipment.
- Consider the Design Carefully: Choose a design that you are confident you will not regret in the future.
- Avoid Impulsivity: Do not rush into getting a tattoo. Take your time to consider your decision and make sure it is something you truly want.
- Consult with Friends and Family: Seek advice from trusted individuals who can provide an objective perspective.
Home Remedies and Self-Care for Unwanted Tattoos
While home remedies may not be effective in completely removing unwanted tattoos, they can help to lighten or fade them to some extent. Some commonly used home remedies include:
- Lemon Juice: Apply lemon juice to the tattoo and leave it on for several hours or overnight.
- Colloidal Oatmeal: Mix colloidal oatmeal with water to form a paste and apply it to the tattoo.
- Aloe Vera Gel: Apply aloe vera gel to the tattoo to soothe and moisturize the skin.
- Salt Scrubs: Scrub the tattoo gently with a mixture of salt and water.
- Hydrogen Peroxide: Apply hydrogen peroxide to the tattoo using a cotton ball.
Impact of Unwanted Tattoos on Daily Life
Unwanted tattoos can have a significant impact on an individual’s daily life, both psychologically and socially. Some of the challenges faced by individuals with unwanted tattoos include:
- Embarrassment and Shame: Feeling self-conscious or ashamed about the tattoo, especially in situations where it is visible.
- Difficulty Finding Employment: Some employers may have policies against visible tattoos, limiting job opportunities.
- Social Stigma: Unwanted tattoos may be perceived negatively by some individuals or communities, leading to social stigma and discrimination.
- Relationship Issues: Unwanted tattoos can cause conflict or tension in relationships, particularly if one partner finds the tattoo unattractive or offensive.
Long-Term Management of Unwanted Tattoos
For individuals with unwanted tattoos that are not completely removable, long-term management involves finding ways to cope with the psychological and social challenges associated with them. This may involve:
- Therapy: Seeking professional counseling or therapy to address feelings of shame, regret, and low self-esteem.
- Support Groups: Joining support groups or online forums where individuals with unwanted tattoos can share their experiences and offer encouragement.
- Body Modification: Considering other forms of body modification, such as scarification or branding, to transform or conceal the unwanted tattoo.
- Acceptance: Ultimately, learning to accept and embrace the unwanted tattoo as a part of one’s personal history and identity.
Mental and Emotional Considerations for Unwanted Tattoos
The psychological impact of unwanted tattoos can be significant, leading to a range of emotions and mental health challenges. Some common issues faced by individuals with unwanted tattoos include:
- Anxiety: Feeling anxious or stressed about the visibility or permanence of the tattoo.
- Depression: Experiencing low mood, loss of interest, and feelings of hopelessness.
- Self-Esteem Issues: Struggling with low self-esteem and body image concerns related to the tattoo.
- Regret: Feeling remorse or guilt over the decision to get the tattoo.
- Fear of Judgment: Worrying about being judged or discriminated against because of the tattoo.
It is important for individuals with unwanted tattoos to seek support from mental health professionals to address these emotional challenges and develop coping mechanisms. Therapy, support groups, and self-care practices can help individuals to manage their feelings and improve their overall well-being.