Understanding Age Spots: An Overview
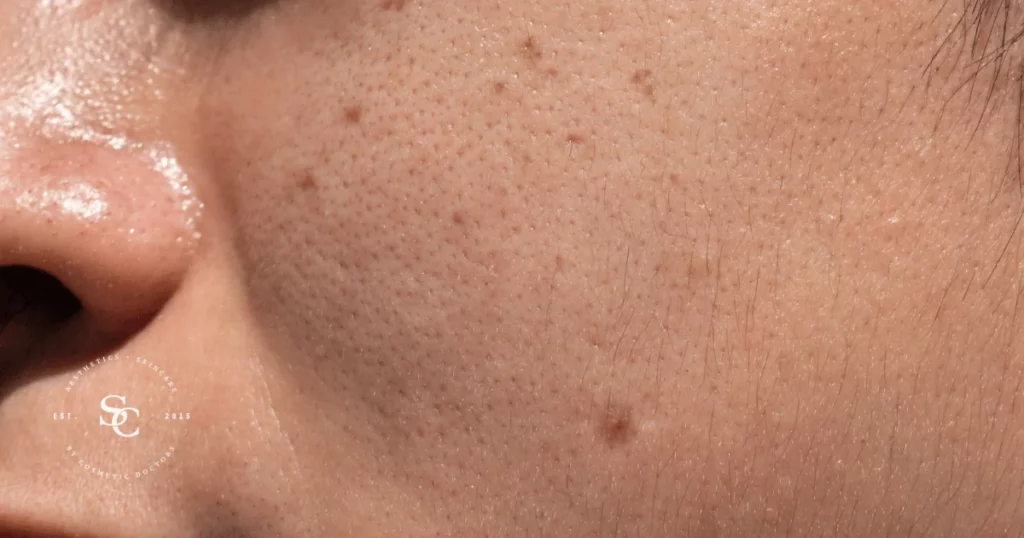
Age spots, also known as liver spots or solar lentigines, are common skin blemishes typically appearing as flat, brown, or grayish patches on the skin. They are associated with aging and prolonged sun exposure. Delve into the world of age spots, exploring their nature, causes, treatments, and prevention strategies for clearer and more youthful skin.
Identifying the Symptoms of Age Spots
The primary symptom of age spots is the presence of flat, discolored patches on the skin, most commonly on sun-exposed areas like the face, hands, shoulders, and arms.
Causes and Risk Factors of Age Spots
Underlying causes and risk factors of age spots include:
- Sun Exposure: Prolonged exposure to UV radiation from the sun is a leading cause of age spots.
- Aging: The natural aging process leads to diminished skin regeneration and repair, making it more prone to pigmentation changes.
- Skin Type: Individuals with fair skin are more susceptible to age spots due to reduced melanin protection.
- Genetics: Genetic factors can predispose individuals to age spots.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, as during pregnancy or menopause, can increase the likelihood of age spot formation.
- Tanning Beds: The use of tanning beds and lamps can contribute to age spots.
Different Types and Stages of Age Spots
Age spots do not have distinct types or stages but vary in size, shape, and color among individuals.
Diagnosis: How Age Spots are Detected
Diagnosing age spots is visual through physical examination by a dermatologist or healthcare provider.
Treatment Options for Age Spots
Several treatment options can reduce the appearance of age spots:
- Topical Treatments: Over-the-counter or prescription creams with ingredients like hydroquinone, retinoids, or glycolic acid can lighten age spots over time.
- Cryotherapy: Liquid nitrogen is applied to freeze and remove age spots.
- Chemical Peels: Chemical peels using alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) or trichloroacetic acid (TCA) can exfoliate the skin, improving the appearance of age spots.
- Laser Therapy: Laser treatments target pigmentation irregularities and stimulate collagen production for a more even skin tone.
- Microdermabrasion: Microdermabrasion procedures exfoliate the skin’s surface, improving the appearance of age spots.
Prevention Strategies for Age Spots
Prevention involves minimizing risk factors:
- Sun Protection: Regularly apply high SPF sunscreen and wear protective clothing to shield the skin from UV radiation.
- Avoid Tanning Beds: Avoid the use of tanning beds and lamps, which can accelerate skin aging and increase the risk of age spots.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking enough water helps maintain skin hydration and overall skin health.
- Protective Clothing: Wear wide-brimmed hats, sunglasses, and long-sleeved clothing when spending time in the sun.
Home Remedies and Self-Care for Age Spots
In addition to medical treatments, self-care practices can help manage age spots:
- Topical Antioxidants: Applying vitamin C or E serums may help protect the skin from further damage.
- Exfoliation: Gentle exfoliation with scrubs or exfoliating brushes can help improve skin texture.
- Skin Hydration: Using moisturizers can help maintain skin hydration and minimize the appearance of age spots.
Impact of Age Spots on Self-Image
Age spots may affect an individual’s self-esteem and body image, particularly if they are prominent or numerous. Addressing age spots can enhance one’s confidence and skin appearance.
Long-Term Management of Age Spots
Managing age spots often involves ongoing care:
- Skincare Routine: Maintain a consistent skincare routine, including sun protection and moisturizing, to support skin health and prevent the worsening of age spots.
- Regular Dermatologist Visits: Periodic visits to a dermatologist can help monitor and manage age spots effectively.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Incorporate a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, hydration, and stress management, to support skin health and minimize the development of new age spots.
Understanding age spots, their causes, treatments, and prevention strategies is crucial for effectively addressing this common skin concern and achieving clearer and more youthful-looking skin. Consulting with a dermatologist or skincare specialist can provide personalized guidance on the most suitable treatments and management approaches for individual concerns.