Understanding Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): An Overview
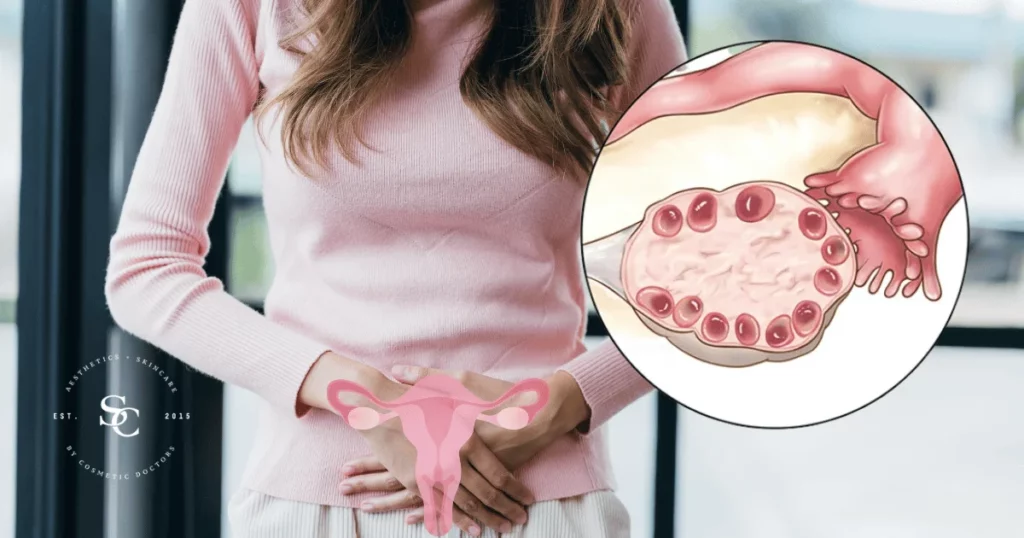
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder that affects people with ovaries, often during their reproductive years. PCOS is characterized by a combination of hormonal imbalances, irregular menstrual cycles, and the presence of small fluid-filled sacs (cysts) on the ovaries.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of PCOS, exploring its nature, general impact, and providing insights into its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and management strategies.
Identifying the Symptoms of PCOS
Symptoms of PCOS can vary among individuals but often include:
- Irregular Menstrual Cycles: Women with PCOS may experience infrequent, prolonged, or absent periods.
- Excess Androgens: Elevated levels of male hormones (androgens) can lead to acne, hirsutism (excessive hair growth), and male-pattern baldness.
- Ovulatory Dysfunction: PCOS can result in anovulation, where the ovaries do not release eggs regularly, contributing to infertility.
- Polycystic Ovaries: The presence of multiple small cysts on the ovaries, as seen on imaging tests.
- Metabolic Issues: Insulin resistance and weight gain are common, increasing the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Causes and Risk Factors of PCOS
The exact cause of PCOS is not fully understood, but several factors contribute to its development:
- Hormonal Imbalances: Elevated levels of androgens and insulin play a central role in PCOS.
- Genetics: A family history of PCOS may increase the risk of developing the condition.
- Insulin Resistance: Many individuals with PCOS have insulin resistance, which can lead to elevated insulin levels and increased androgen production.
Diagnosis: How PCOS is Detected
Diagnosing PCOS involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests, including:
- Pelvic Ultrasound: To visualize the ovaries and check for cysts.
- Blood Tests: To measure hormone levels, including androgens and insulin.
- Menstrual History: Evaluating the frequency and regularity of menstrual cycles.
- Physical Examination: Assessing for physical signs of PCOS, such as hirsutism or acne.
Treatment Options for PCOS
Treatment for PCOS is tailored to individual symptoms and goals:
- Lifestyle Changes: Managing weight through diet and exercise can improve insulin sensitivity and reduce symptoms.
- Hormonal Birth Control: Oral contraceptives can regulate menstrual cycles and manage androgen-related symptoms.
- Anti-Androgen Medications: Spironolactone or finasteride may be prescribed to reduce hirsutism and acne.
- Fertility Treatments: For those trying to conceive, fertility medications like clomiphene or assisted reproductive technologies (ART) may be recommended.
- Metformin: An insulin-sensitizing medication that can help manage metabolic issues and regulate menstrual cycles.
- Surgery: In some cases, ovarian drilling or ovarian wedge resection may be considered to induce ovulation.
Management and Prevention Strategies for PCOS
Managing PCOS involves a holistic approach to address its various aspects:
- Regular Monitoring: Continuously tracking symptoms, hormone levels, and metabolic markers.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise is essential in managing PCOS and reducing insulin resistance.
- Nutritional Counseling: Consult with a registered dietitian to develop a balanced eating plan that supports insulin regulation.
- Stress Reduction: Stress management techniques, such as meditation or yoga, can help mitigate hormonal fluctuations.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in physical activity can improve insulin sensitivity and overall health.
Impact of PCOS on Daily Life
PCOS can have physical, emotional, and lifestyle implications:
- Fertility Challenges: PCOS is a leading cause of infertility in people with ovaries.
- Hormonal Symptoms: Acne, hirsutism, and male-pattern baldness can affect self-esteem.
- Metabolic Risks: Insulin resistance may lead to weight gain and increase the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Long-Term Management of PCOS
Managing PCOS often involves ongoing care and monitoring:
- Fertility Planning: For individuals planning to have children, working with a reproductive specialist can optimize fertility treatments.
- Hormonal Balance: Continual management of hormonal symptoms and metabolic health.
- Emotional Support: Seek support from therapists or support groups to cope with the emotional aspects of living with PCOS.
- Regular Check-Ups: Consistent follow-up with healthcare providers for routine monitoring.
In conclusion, understanding PCOS, its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, management strategies, and its impact on daily life is crucial for effective management and overall well-being. Seeking professional guidance and support can significantly contribute to living a fulfilling life with PCOS.