Understanding Ingrown Hairs: An Overview
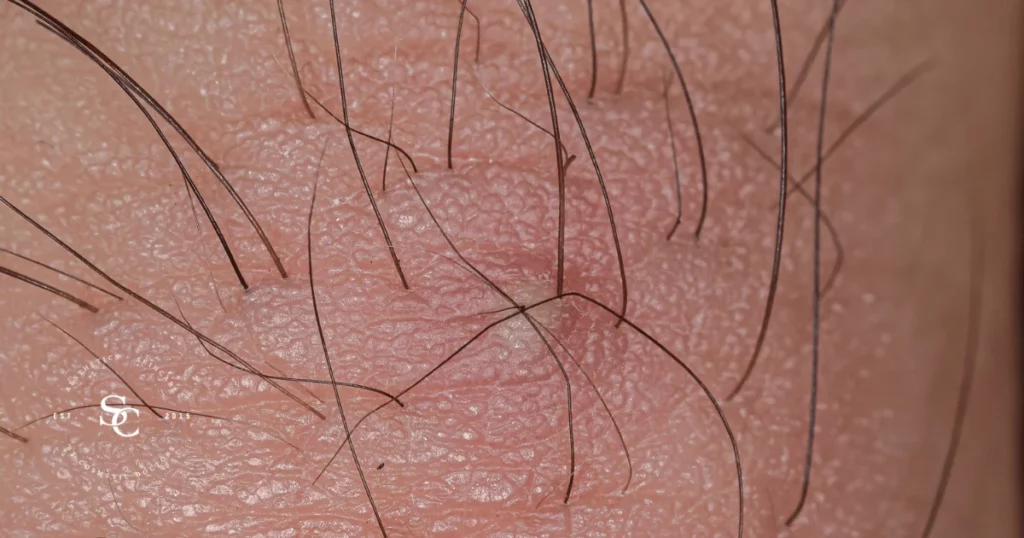
Ingrown hairs are a common skin condition that occurs when a hair curls back or grows sideways into the skin instead of emerging from the hair follicle. This can lead to painful red bumps and irritation. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of ingrown hairs, exploring their nature, causes, treatment options, prevention strategies, and skincare considerations.
Identifying the Symptoms of Ingrown Hairs
The primary symptom of ingrown hairs is the presence of raised, red bumps or pustules on the skin, often accompanied by itching, tenderness, and discomfort. Ingrown hairs can occur anywhere on the body where hair grows.
Causes and Risk Factors of Ingrown Hairs
Understanding the causes and risk factors of ingrown hairs is essential:
- Hair Removal Methods: Shaving, waxing, plucking, and threading can increase the risk of ingrown hairs, as they alter the natural hair growth pattern.
- Curly or Coarse Hair: Individuals with curly or coarse hair are more prone to ingrown hairs, as their hair may have a tendency to curl back into the skin.
- Tight Clothing: Wearing tight clothing can create friction against the skin and lead to ingrown hairs, especially in areas like the groin or underarms.
- Improper Skincare: Poor skincare practices, such as lack of exfoliation or moisturization, can contribute to the development of ingrown hairs.
Different Types and Stages of Ingrown Hairs
Ingrown hairs typically do not have distinct types or stages but can vary in severity and appearance.
Diagnosis: How Ingrown Hairs are Detected
Diagnosing ingrown hairs is straightforward, as they can often be identified through visual examination by a healthcare provider or dermatologist. No specialized tests are needed.
Treatment Options for Ingrown Hairs
Several treatment options can help alleviate the discomfort and appearance of ingrown hairs:
- Topical Antibiotics: Over-the-counter or prescription topical antibiotics can help prevent or treat infection associated with ingrown hairs.
- Topical Steroids: Steroid creams can reduce inflammation and ease itching.
- Exfoliation: Regular exfoliation with a gentle scrub or exfoliating products can help prevent and treat ingrown hairs by removing dead skin cells.
- Warm Compress: Applying a warm compress can help soothe irritated skin and encourage the hair to surface.
- Avoid Hair Removal: Temporarily discontinuing hair removal methods in the affected area can allow the hair to grow out naturally.
Prevention Strategies for Ingrown Hairs
Preventing ingrown hairs involves adopting good skincare and hair removal practices:
- Proper Exfoliation: Regular exfoliation with a mild scrub or chemical exfoliant helps prevent the buildup of dead skin cells.
- Moisturization: Keeping the skin well-hydrated with a non-comedogenic moisturizer can reduce friction and irritation.
- Hair Removal Techniques: Consider alternative hair removal methods, such as laser hair removal, which can reduce the risk of ingrown hairs.
- Sharp Razors: Use a sharp, clean razor when shaving, and shave in the direction of hair growth.
- Loose Clothing: Wear loose-fitting clothing to reduce friction in areas prone to ingrown hairs.
Home Remedies and Self-Care for Ingrown Hairs
While professional treatment may be necessary in some cases, there are home remedies and self-care practices that can help:
- Warm Soaks: Soak the affected area in warm water to soften the skin and hair, making it easier to release the ingrown hair.
- Avoid Picking: Refrain from picking or digging into ingrown hairs, as this can lead to infection and scarring.
- Over-the-Counter Treatments: Over-the-counter treatments containing salicylic acid or glycolic acid can help exfoliate the skin and prevent ingrown hairs.
Impact of Ingrown Hairs on Skin Health
Ingrown hairs are typically a minor skin concern that may cause discomfort and cosmetic issues. However, in some cases, they can become infected, leading to more severe complications.
Long-Term Management of Ingrown Hairs
Managing ingrown hairs often involves ongoing skincare and hair removal practices:
- Regular Exfoliation: Continue exfoliating the skin to prevent the buildup of dead skin cells.
- Hydration: Maintain skin hydration with a moisturizer to reduce friction.
- Professional Hair Removal: Consider long-term hair removal methods like laser hair removal if ingrown hairs persist.
In conclusion, understanding ingrown hairs, their causes, treatment options, prevention strategies, and skincare practices is essential for effective management and maintaining healthy, irritation-free skin. Consulting with a healthcare provider or dermatologist can provide guidance on the most suitable treatments for individual concerns.